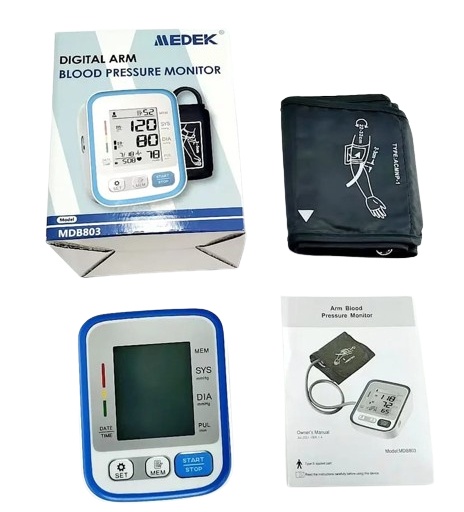
Blood pressure is typically measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) and is represented as two numbers:
- Systolic Pressure: This is the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats and pumps blood out.
- Diastolic Pressure: This is the pressure in your arteries when your heart rests between beats.
Here’s a general chart to interpret blood pressure readings for adults:
- Normal:
- Systolic: Less than 120 mmHg
- Diastolic: Less than 80 mmHg
- Elevated:
- Systolic: 120-129 mmHg
- Diastolic: Less than 80 mmHg
- Hypertension Stage 1:
- Systolic: 130-139 mmHg
- Diastolic: 80-89 mmHg
- Hypertension Stage 2:
- Systolic: 140 mmHg or higher
- Diastolic: 90 mmHg or higher
- Hypertensive Crisis (Emergency care needed):
- Systolic: Higher than 180 mmHg
- Diastolic: Higher than 120 mmHg
It’s essential to note that a single high reading doesn’t necessarily mean you have high blood pressure. If you consistently have readings above the normal range, it’s crucial to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation and guidance.