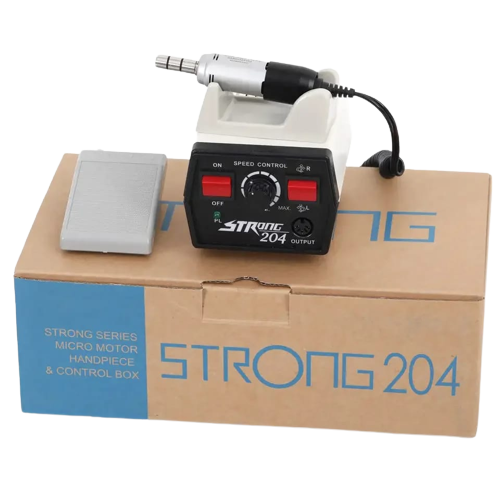
A dental micromotor is a compact, high-speed rotary device used in dentistry to drive handpieces for various procedures. It’s a critical part of the dental delivery system and is especially used in restorative, endodontic, and surgical dental work.
✅ Definition
A dental micromotor is an electrically or air-powered motor used to rotate dental instruments (like burs or polishers) at variable speeds for cutting, grinding, polishing, or drilling tasks.
⚙️ Key Features
- Speed Control:
- Adjustable rotation speeds (typically between 1,000 to 40,000 RPM or higher).
- Allows precision for different procedures.
- Torque:
- Provides high torque at low speeds, useful for cutting and polishing hard materials.
- Motor Type:
- Electric micromotors: Offer constant speed and torque.
- Air-driven micromotors: Cheaper, but with variable performance depending on air supply.
- Ergonomics:
- Lightweight handpiece for better control and reduced fatigue.
- Often comes with foot pedals for hands-free operation.
- Cooling System:
- Built-in air or water cooling to prevent overheating.
- Compatibility:
- Connects with a range of contra-angle or straight handpieces.
- Noise & Vibration:
- Designed for low noise and minimal vibration for patient comfort.
🦷 Common Uses in Dentistry
- Tooth Preparation:
- For removing decay and shaping cavities before filling.
- Prosthodontics:
- Trimming crowns, bridges, and denture bases.
- Endodontics:
- Canal preparation with rotary endo files.
- Oral Surgery:
- Cutting bone or sectioning teeth during extraction.
- Polishing:
- Smoothing tooth surfaces and prostheses.
- Laboratory Work:
- Used in dental labs for grinding, polishing, and finishing appliances.
📌 Summary
| Feature | Details |
|---|---|
| Type | Electric or air-driven |
| Speed Range | ~1,000 to 40,000+ RPM |
| Uses | Cutting, grinding, polishing, root canal prep |
| Advantages | Precise, quiet, efficient, ergonomic |