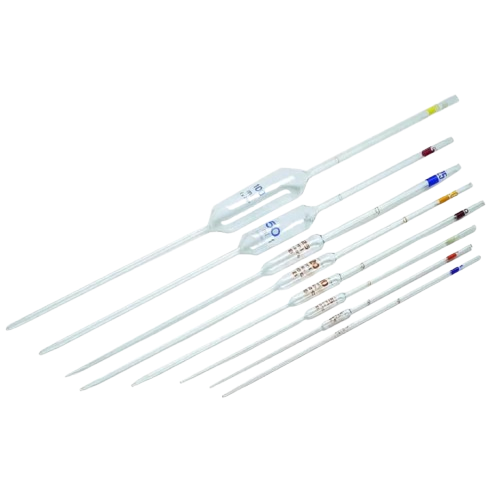
A laboratory volumetric pipette is a precise instrument used to measure and transfer a specific volume of liquid in a laboratory setting. It is widely used in analytical chemistry, biology, and medical laboratories where accurate liquid measurement is crucial.
Features of a Volumetric Pipette:
- Precision: Designed to deliver a single, specific volume of liquid with high accuracy (e.g., 5 mL, 10 mL, 25 mL, etc.).
- Bulb Shape: The pipette has a bulb in the middle of its body, which enhances its precision by minimizing the effect of temperature changes on the liquid volume.
- Calibrated Mark: A single calibration mark indicates the exact volume the pipette can measure when filled to that line.
- Narrow Tip: Ensures controlled and precise delivery of the liquid.
- Material: Usually made of borosilicate glass or high-quality plastic for durability and chemical resistance.
Usage:
- Clean the pipette thoroughly to avoid contamination.
- Fill the pipette using a pipette filler or bulb until the liquid slightly exceeds the calibration mark.
- Adjust the liquid level precisely to the calibration mark by carefully releasing excess liquid.
- Deliver the liquid by touching the tip to the receiving container and allowing gravity to drain it. Some pipettes require you to blow out the remaining liquid for complete delivery.
Types of Volumetric Pipettes:
- Class A: High accuracy, used for critical measurements.
- Class B: Slightly less accurate, suitable for routine work.
Applications:
- Preparing standard solutions.
- Diluting samples.
- Quantitative chemical analysis (e.g., titration).
Proper handling and calibration are essential to maintain the accuracy and reliability of volumetric pipettes.


There are no reviews yet.